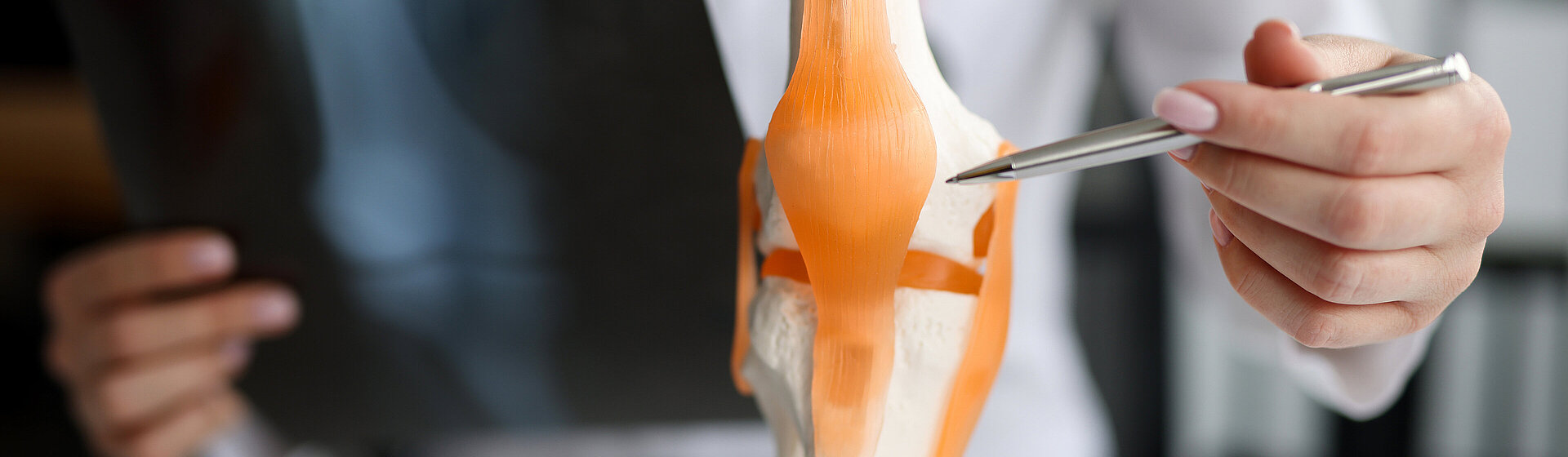
The cartilage acts as a buffer, is elastically deformable and can absorb shocks, for example when walking. However, accidents or wear and tear can cause damage to the cartilage. The causes of such cartilage damage are varied. In addition to a genetic predisposition, obesity, for example, is a risk factor and meniscus or cruciate ligament injuries also promote cartilage damage.
Symptoms of cartilage damage
As cartilage has no nerve fibers, the patient usually feels very little at the beginning. However, the symptoms increase with progression and inflammation. The cartilage damage then manifests itself as a crunching sensation, swelling or pain on exertion. The joint can even hurt when at rest. As the tissue is not supplied with blood, there is little potential for regeneration - spontaneous healing is impossible. On the contrary, symptoms increase over time.
Therapy: How cartilage damage is treated
Although conservative treatment options are possible, these are purely symptomatic treatment. Healing, on the other hand, can only be achieved surgically. Various surgical methods, including cell transplantation, are available to restore the cartilage cover. However, if osteoarthritis (wear and tear) has already developed, surgical treatment is generally no longer possible. Therefore, the earlier it is recognized and treated, the greater the chances of recovery.
Preventing cartilage damage
The good news is that a healthy lifestyle can prevent damage. It is important to avoid being overweight and to keep moving. Like muscles, cartilage can also be "trained". Studies have shown that the thickness of the cartilage layer decreases when it is relieved or protected. After a longer break from sport, those affected should therefore gradually build up the load again.
Diet also plays a role. Gluco-samine and chondroitin sulphate are important components of this cartilage tissue. These substances are contained in seafood or can be obtained from certain dietary supplements.
However, the most important principle remains: if you rest, you rust - so watch your weight and keep moving!

Dagmar Alms
Secretariat Shoulder, elbow, knee surgery and traumatology
- Phone+49 2351 945-2305
- Fax +49 2351 945-2307
- sekretariat.leyh@hellersen.de

Kerstin Funk-Niklas
Secretariat for knee surgery and sports traumatology
- Phone+49 2351 945-2236
- Fax +49 2351 945-2237
- sekretariat.stoll@hellersen.de
Private outpatient clinic
Phone +492351 945-2236
Fax +492351 945-2237
sekretariat.stoll@hellersen.de